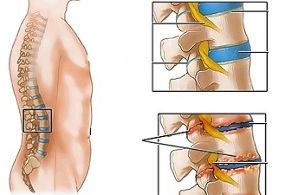
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a chronic disease that develops as a result of a degenerative-dystrophic process in the intervertebral discs. The disease is widespread and affects most people between the ages of 25 and 40.
According to statistics, every second an adult experiences back pain at least once in his life, while in 95% of cases it is caused by osteochondrosis of the spine.
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a serious medical and social problem, as the disease mainly affects older people and, in the absence of treatment, can cause disc herniation.Patients with severe osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, with persistent pain and other manifestations, are recognized as temporary disabilities. If their condition does not improve within four months, the issue of setting up a disability group is decided.
Causes and risk factors
Factors that predispose to the development of bone osteochondrosis are:
- abnormalities of the structure of the spine?
- low back pain - a congenital pathology of the spine, characterized by the separation of the first vertebra from the sacrum and its transformation into the sixth (additional) lumbar tissue.
- hierarchy is a congenital pathology in which the fifth lumbar vertebra merges with the sacrum.
- asymmetric arrangement of the joints of the intervertebral joints.
- pathological narrowing of the spinal canal.
- reflects spondiogenic pain (physical and muscle).
- obesity?
- sedentary lifestyle
- prolonged exposure to vibration.
- systemic physical stress.
- smoking.
Prolonged compression of nerve roots that hydrate certain abdominal organs over time leads to a deterioration in their function.
Spinal instability is accompanied by reactive changes in the bodies of adjacent vertebrae, intervertebral joints and the simultaneous development of a vertebral joint. A significant contraction of the muscles, for example, in the context of physical exercise, leads to displacement of the vertebral bodies and entrapment of the nerve roots with the development of root syndrome.
Another cause of pain and neurological symptoms in lumbar osteochondrosis may be osteophytes - bone growths in the processes and vertebral bodies that cause rhizome syndrome or compression myelopathy (spinal cord compression).
Forms of the disease
Depending on which structures are involved in the pathological process, lumbar osteochondrosis is clinically manifested by the following syndromes:
- reflex- lumbodynia, lumboishalgia, lumbago; develop in the context of reflex hyperactivity of the back muscles.
- compression (spine, vascular, radial)- compression (compression) of the spinal cord, blood vessels or nerve roots leads to their development. Examples are sciatica, radical ischemia
Symptoms of bone osteochondrosis
In lumbar osteochondrosis, the symptoms are determined by which structures are involved in the pathological process.
Lumbago occurs under the influence of hypothermia or physical overeating, and sometimes for no apparent reason. The pain appears suddenly and has a shooting character. Intensifies during sneezing, coughing, body twisting, exercise, sitting, standing, walking. In the supine position, the sensations of pain are significantly attenuated. Sensitivity and reflexes are maintained, the range of motion in the lumbar spine is reduced.
Notice the touch:
- lumbar pain?
- spasm of the paraspinal muscles.
- flattening of the lumbar lordosis, which in many cases is associated with scoliosis.
Nerve root tension syndrome in back pain is negative. When lifting a straight leg, patients notice an increase in lumbar pain rather than an appearance in an extended lower limb.
Often, with lumbar osteochondrosis, a recurrence of pain attacks occurs, which each time becomes more intense and prolonged.
In low back pain, the clinical picture is similar to back pain, but the increase in pain intensity occurs for several days.
With low back pain, patients complain of pain in the lumbar region that radiates to one or both lower extremities. The pain spreads to the buttocks and the back of the thigh and never reaches the legs.Lumboishalgia is characterized by vasomotor disorders:
- changes in temperature and skin color of the lower extremities.
- feeling hot or cold.
- blood circulation disorder.
The development of lumbar compression syndromes is clinically manifested by the following symptoms:
- skin hypalgia?
- download pains?
- attenuation or complete loss of deep reflexes.
- peripheral paralysis.
With compression syndromes, the pain is aggravated by torso flexion, sneezing and coughing.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of osteochondrosis is based on the clinical picture of the disease, laboratory and organic research methods
In blood tests in the context of lumbar osteochondrosis:
- decrease in calcium concentration?
- increased ESR.
- increased alkaline phosphatase levels.
In the diagnosis of bone osteochondrosis, great importance is attached to the radiographic examination of the spine.
Prolonged compression of nerve roots that hydrate certain abdominal organs over time leads to a deterioration in their function.
X-ray signs confirming the diagnosis are:
- change the configuration of the affected part.
- pseudospinal slip (displacement of adjacent vertebral bodies);
- deformation of the closing plates.
- leveling of the intervertebral disc?
- unequal height of the intervertebral disc (separator symptom), which is associated with asymmetric muscle tone.
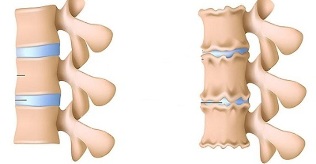
Also, in the diagnosis of bone osteochondrosis, if appropriate, the following are used:
- myelography, computed tomography or MRI - are necessary for persistent symptoms, development of neurological deficits.
- scintigraphy (study of phosphorus accumulation from the bone system, labeled tech-99) - is performed if a tumor or infectious process or spinal cord injury is suspected.
The differential diagnosis of bone osteochondrosis is made with the following diseases:
- spondylolisthesis?
- deformed vertebral disease?
- ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis);
- infectious processes (inflammation of the disc, osteomyelitis of the spine);
- neoplastic processes (primary spinal tumor or metastatic lesions)
- rheumatoid arthritis?
- deformity of osteoarthritis of the hip joint.
- reflex pain (diseases of internal organs and large blood vessels).
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
For lumbar osteochondrosis, the following treatment regimens are usually followed:
- Bed rest for 2-3 days.
- traction of the affected part of the spine.
- Strengthening the muscles of the back and abdominal muscles (creation of the so-called muscle corset).
- effect on abnormal myofascial and myotonic processes.
Lumbago occurs under the influence of hypothermia or physical overeating, and sometimes for no apparent reason.
In most cases, conservative treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis is performed, including the following:
- muscle penetration anesthesia with local anesthetic solution.
- taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- taking desensitizing agents?
- vitamin therapy?
- taking sedatives and antidepressants.
- manual treatment, massage?
- physiotherapy exercises?
- acupuncture?
- post-isometric relaxation.
The absolute indications for surgical treatment of bone osteochondrosis are:
- acute or subacute spinal cord compression?
- development of cauda equina syndrome, characterized by pelvic organ dysfunction, sensory and motor disorders.
Therapeutic exercises for lumbar osteochondrosis
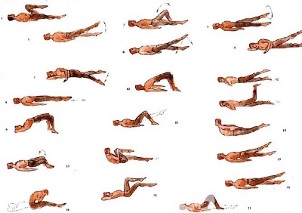
Physical therapy plays an important role in the complex treatment of bone osteochondrosis. Regular exercises allow you to normalize the muscle tone of the paravertebral muscles, to improve the metabolic processes in the tissues affected by the pathological process and in addition to form a well-developed muscular corset that can support the spine in the right position, relieveunnecessary loads from him.
In order for gymnastics for lumbar osteochondrosis to have the greatest effect, the following principles must be observed:
- regularity of courses?
- gradually increase the intensity of physical activity.
- Avoid overwork during the lesson.
Physiotherapy should be performed under the guidance of an experienced instructor, who will select the exercises that are most effective for a particular patient and will check the correctness of its application.
According to statistics, every second an adult experiences back pain at least once in his life, while in 95% of cases it is caused by osteochondrosis of the spine.
In addition to classes with an instructor, you will need to do a series of morning exercises daily, which include special exercises for lumbar osteochondrosis.
- Relaxation and contraction of the abdominal muscles.The starting position is upright, feet shoulder-width apart, arms below the body. Take a deep breath, relaxing the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. On the exhale, pull the stomach as far as it will go, stretching the abdominal muscles. Exercise should be repeated until mild fatigue occurs.
- Head movements with bending of the spine.The starting position is kneeling, leaning on the floor with outstretched arms, back straight. Slowly raise your head and bend at your back. Hold this position for a few seconds and then return smoothly to the starting position. Repeat at least 10-12 times.
- "Pending".The starting position is on your back, arms along the body, legs bent at right angles to the knee and hip joints. Turn your legs left and right on moving pendulums, trying to reach the floor. In this case, the shoulders can not be torn from the floor.
- Boat.The starting position is on your stomach, arms extended forward. Cut the upper body and legs off the floor, bending at the back. Hold this position for 5-6 seconds and slowly return to the starting position. Perform 10 times.
Possible consequences and complications
The main complications of bone osteochondrosis are:
- intervertebral hernia formation?
- vegetative-vascular dystonia?
- spondylolysis, spondylolisthesis?
- osteophytosis?
- vertebral joints?
- narrowing of the spinal canal, which leads to compression of the spinal cord and can cause permanent disability and reduced quality of life.
Prediction
Lumbar osteochondrosis pain syndrome occurs in the form of remission and exacerbations. Lumbago lasts 10-15 days, after which the patient's condition improves, the pain subsides. A favorable outcome can be prevented by associated secondary diseases. Often, with lumbar osteochondrosis, there is a recurrence of pain attacks, which each time become more intense and prolonged.
Patients with a severe course of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, with persistent pain and other manifestations, are recognized as temporary persons with disabilities. If their condition does not improve within four months, the issue of setting up a disability group is decided.Physical therapy plays an important role in the complex treatment of bone osteochondrosis.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of osteochondrosis of the spine consists of the following measures:
- smoking cessation.
- normalization of body weight?
- improvement of the general physical condition, of the active way of life.
- avoid provocative conditions (weight lifting, sudden movements, turns, turns).












































